
JIRA is generally designed for software program development, however, a way to its workflow control system is very good and it has been applied as an assignment control answer through many assignment groups.
Atlassian’s Jira software program sticks out amongst assignment control collaboration gear due to its popularity, especially in the records technology (IT) industry. It’s designed specifically for groups using an agile assignment control methodology, making Jira’s agile gear herbal in shape for IT.
Overview :
- In today’s world, the majority of IT users know about Jira. It commenced as an IT tool, however, now it has many uses, from conventional assignment control to an IT ticketing system. It covers the assignment control fundamentals with a complete gear suite, along with assignment making plans, mission advent, and control, and reporting.
- Any user can project the Jira mission by listing on a display screen while we meet for dash-making plans and unique agile events, and it works fantastically to get users on a similar page while we streamline those meetings.
Following are the best capabilities for any user to manage projects in JIRA:
- Best use for agile planning from assignment backlog to sprints.
- Fully customizable boards.
- The cap potential to estimate time for problems as users will prioritize your backlog.
- Number of reports are available starting from burndown charts to pace measurements.
- Customizable workflows to suit your frameworks.
Use of Jira for project management:
Below are the steps to summarize the important elements of JIRA for dealing with the projects:
Step 1: Project configuration
- Choose a Jira template to install specific user projects. Templates are a short aspect to configure your assignment primarily based on the procedures used at your organization.
- For instance, the User can utilize the assignment control, choose the kanban template, and Jira will install a default kanban board and workflows. Users can then install any assignment/project.
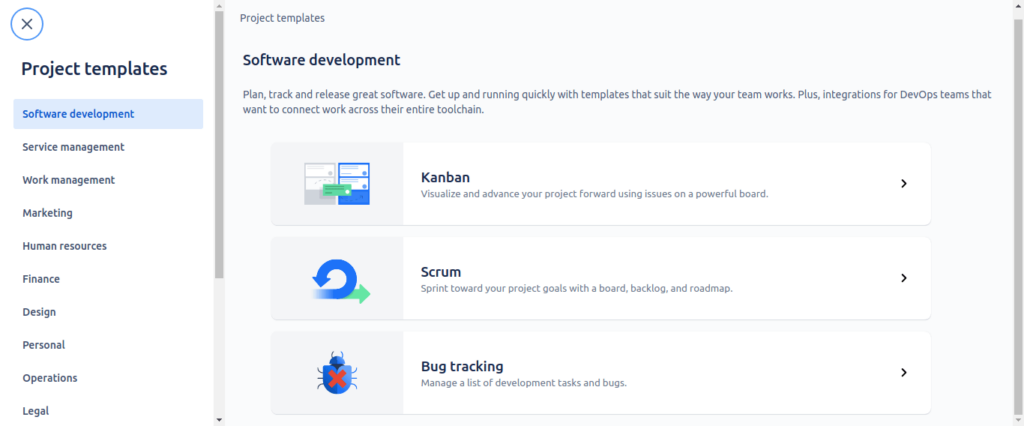
Choose a project type
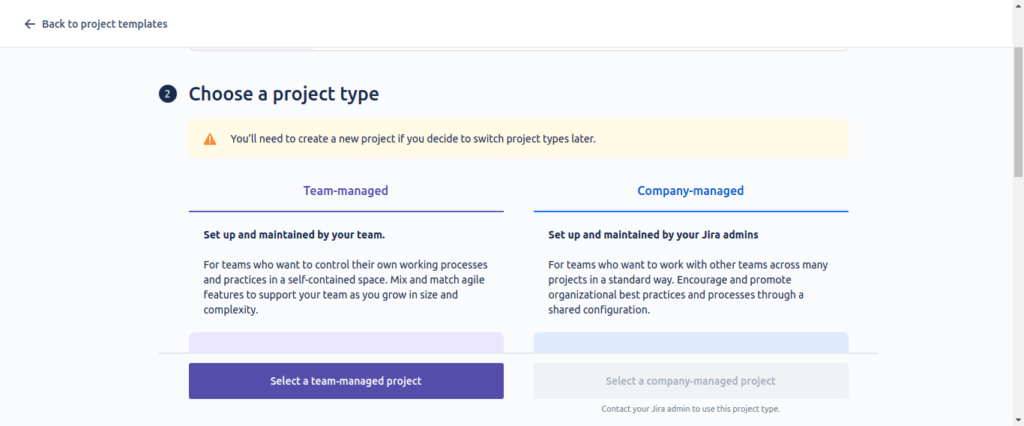
Create a Project

Step 2: Creating RoadMap
- A road map may be a strategic plan that defines a goal or desired outcome and includes the main steps or milestones needed to achieve it. It also is a communication tool, a high-level document that helps articulate strategic thinking—the why—behind both the goal and also the plan for getting there.
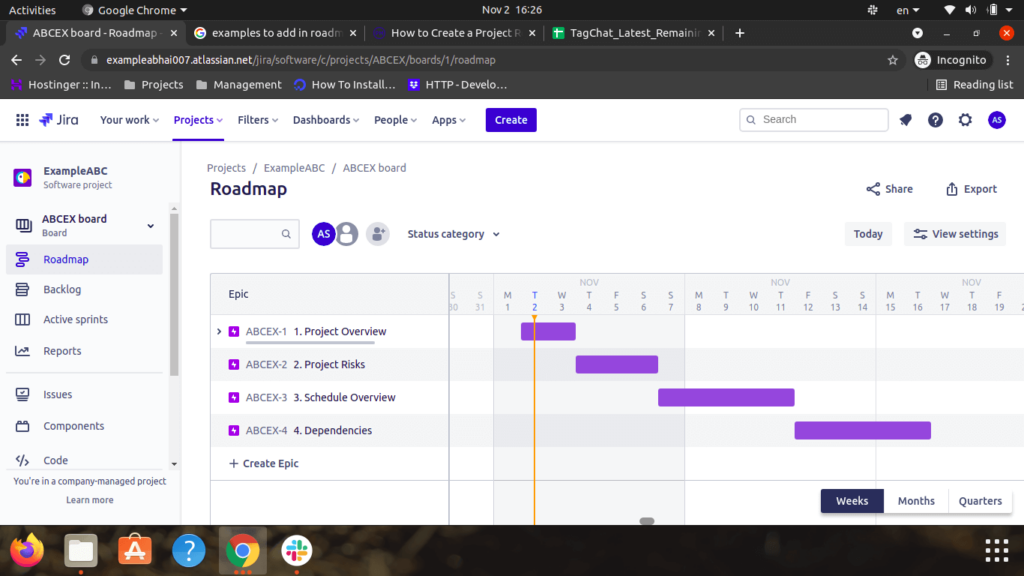
Below are the key points to form a roadmap:
- The first user needs to create an Issue in JIRA
- In the issue, the user can enter multiple details like assignee, report name, story points, time tracking, sprints, etc.

- In the issue, the user also can create multiple tasks. In a single task, the user can add task descriptions, attachments, links, assignee, report names, story points, time tracking, sprints, etc.
- Users may share and export the particular Road Map
Step 3: Backlogs
- A backlog could be a set of activities or issues that the team must resolve within a selected iteration. All the problems of your project are grouped during a backlog and sprint.
- List of tasks that represent outstanding adds a project.

- Users can view the tasks within the backlog. Users may create issues within the backlog.
- There is a choice to drag one issue from one place to a different supported priority.
- In Backlog, the User will have the choice to make the sprint.
- In the sprint, the user will add duration, start date, end date, and goal associated with the sprint.

- We can move all the backlog tasks into the created sprint and therefore the user should start the sprint.
Step 4: Sprints
- The sprints within the board display the problems that your team is currently performing on. You’ll create and update issues, and drag and drop issues to transition them through a workflow.
- Sprints make projects more manageable, allow teams to ship high-quality work faster and more frequently, and provide them more flexibility to adapt to vary. Many users work on the scrum sprints with agile software development, which is often to be the identical thing.
- In Jira Software, sprints are planned on the Backlog screen.
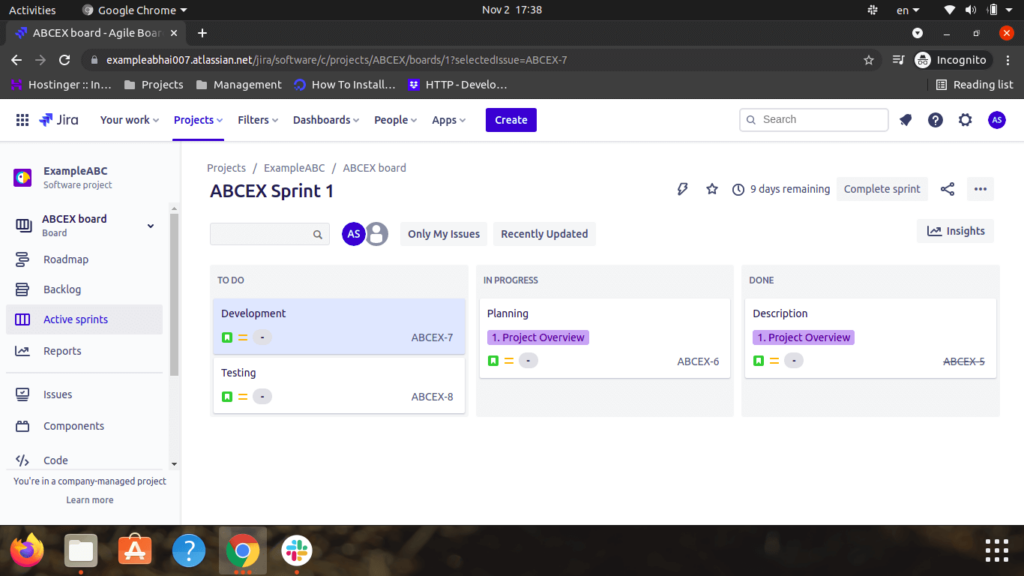
- After all the tasks are completed, the user will have the choice to finish the sprint. Users may also share the tasks and sprints by copying the link.
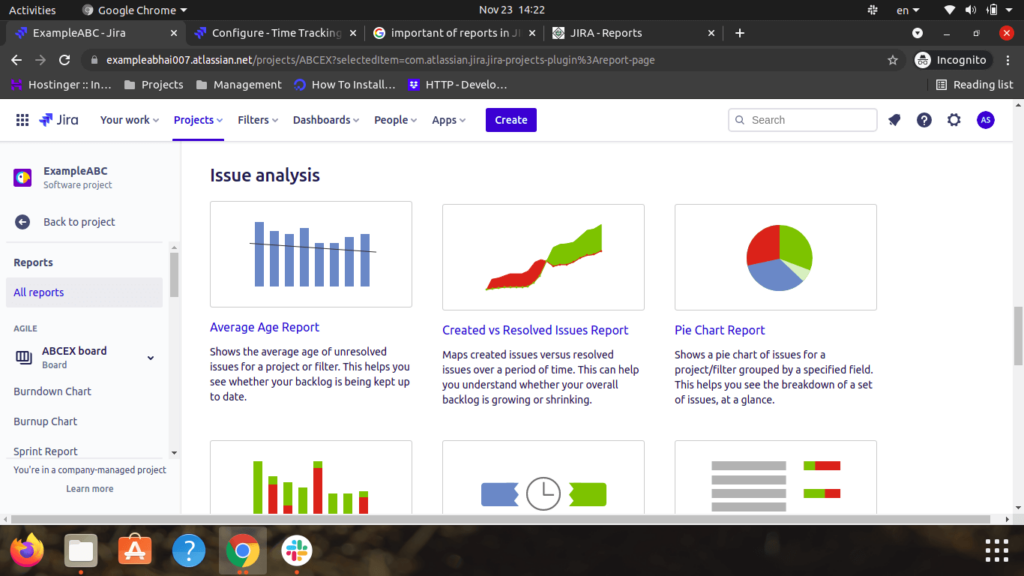
Step 5: Reports
- Users can create multiple reports for one project. It’ll help the user to investigate the performance, progress, and manage the timeline of the project.
- By clicking on the Report icon on the left side of the page, it will display all the reports supported by JIRA. It’ll be categorized into four types:
- Agile
- Issue Analysis
- Forecast & Management
- Others
- By clicking on the Report icon on the left side of the page, it will display all the reports supported by JIRA. It’ll be categorized into four types:
Below are the few images for the reports, users can use within the projects:
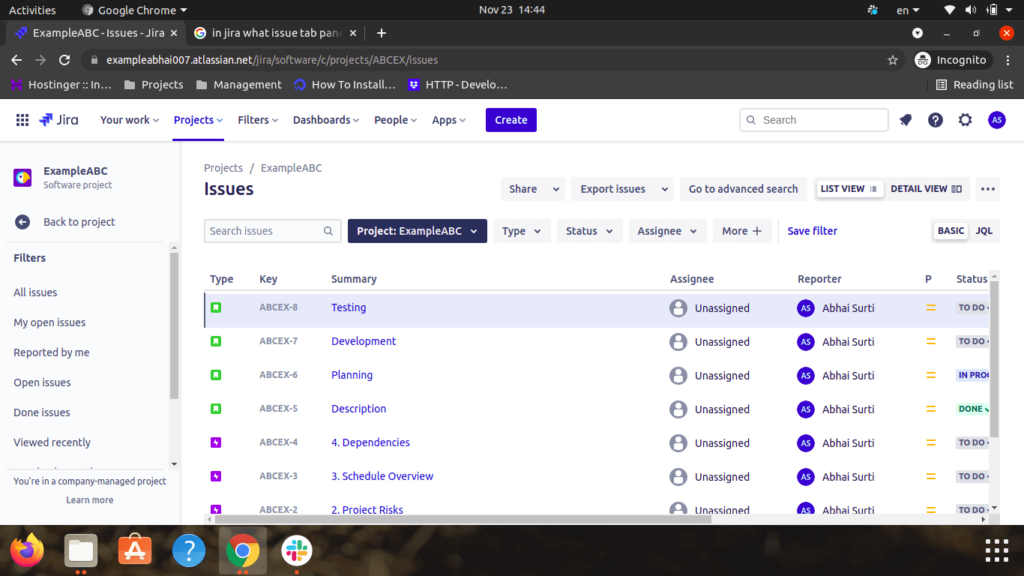
Step 6: Issues
In Jira, users use issues to trace the individual tasks of labor that have to be completed. Depending on how the user uses Jira, a problem could represent a project task, a ticket, a story, a bug, etc. within the project.
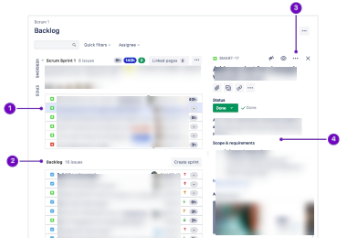
There will be four sorts of issues:
- Selected issue: Select a problem to look at its details.
- Backlog: Estimate issues and plan your sprints.
- Issue actions: Pass the difficult task, clone it, log time spent acting on it, and perform other actions.
- Issue details: See the assignee and outline, make comments, and add content to the problem.
Step 7: Code
- The Code feature gives you greater visibility of your team’s work by automatically linking and displaying your team’s code repositories in your project.
- Users can enable the code supported on the below points:
- Navigate the user to manage the project.
- Open Project Settings and Click on the Features.
- The user will have to enable the Code feature then after it will be useful.
- In the code, a new menu item is being added to the project menu.
- Users can enable the code supported on the below points:
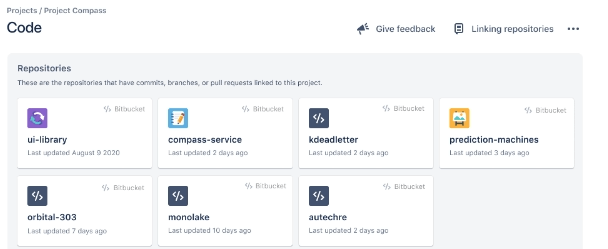
- The Code screen will display an inventory of the repositories where your team’s work would be related to this project.
Step 8: Project Pages
- It is useful for creating, storing & sharing all project-related documentation. Project Pages is the one place within the user Jira project where users can see all of the relevant Confluence pages, the team is creating. It also provides quick shortcuts to form the kinds of documents most useful to your team.
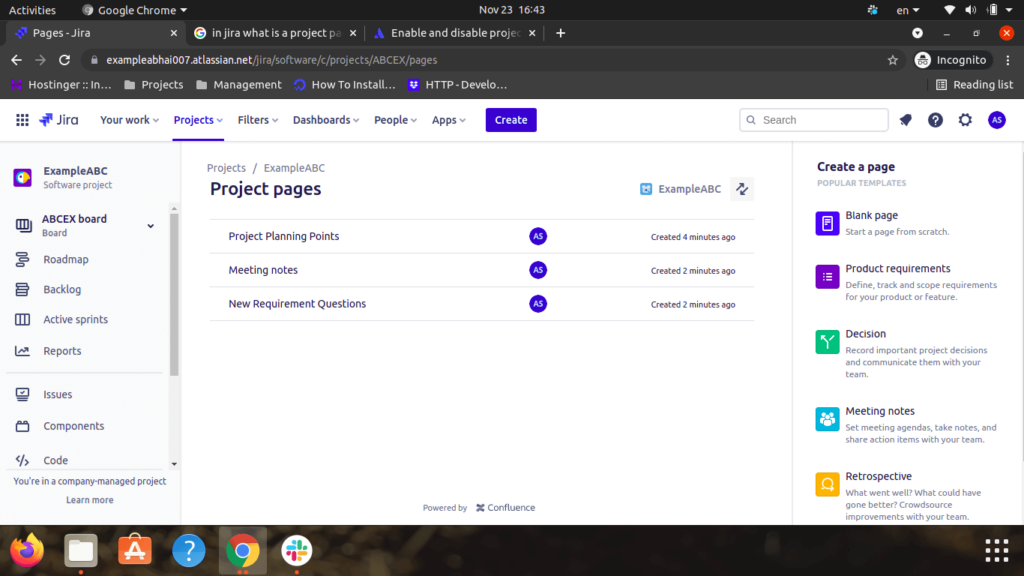
- In the project menu, select Project pages and then select one among the templates if the user wishes to get started, or select Blank page to make a page from scratch. Whichever option you choose, you will be taken to Confluence to form your page.

Note: There are many other features available in JIRA to manage the projects. But here you’ll be able to see the common features which are being used by many users to manage their projects.
Conclusion:
JIRA could be a more important and powerful tool that’s optimized for agile and managing projects. JIRA offers many positives and benefits to the users from managing project tasks to tracking bugs, to providing customer support.
JIRA also works great for smaller teams, as well as larger ones. JIRA will be super useful since it’s scalable when the business grows.
Related Blogs
App Development
appstonelab

App DevelopmentSaaS
appstonelab

